Mud Motor 5LZ95
| 产品参数 Products Specification 5LZ95 | ||
| 钻头外径 Dia. of Bit | mm | 118~152 |
| inch | 4 5/8~6 | |
| 扣型(REG) Thread(REG) | 3 1/2 REG female 2 7/8 IF male | |
| 重量 毛/净(kg) Weight G/N(kg) | 180/180 | |
| 流速 (L/s) Rate of Fow (L/s) | 5~11 | |
| 压差 (Mpa) Diff. pressure (Mpa) | 3.2 | |
| 工作扭矩(N.m)Working torque (N.m) | 970 | |
| 最大扭矩(N.m)Max. torque (N.m) | 1750 | |
| 长度 (mm) Length (mm) | 4470 | |
| 工作钻压 (KN)Working WOB (KN) | 25 | |
| 级数 Stage Number | 4 | |
Brief Introduction of Mud Motor
Mud motors are essential tools in trenchless construction, particularly in Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD). They rotate the drill bit at the end of the drill string, allowing us to bore underground without open excavation.
1. Function (作用):
Rotating the Drill Bit (旋转钻头): The primary function of a mud motor is to power the drill bit rotation. Unlike rotary drilling where the entire drill string is rotated from the surface, in HDD with mud motors, only the drill bit rotates. This is crucial for directional control and efficiency.
Directional Drilling (定向钻进): Mud motors are key for steering the drill bit along a planned path. By combining the mud motor with a slightly bent housing and directional drilling tools, operators can precisely control the drilling direction to go around obstacles and reach target locations underground.
Powered by Mud (泥浆驱动): As the name suggests, mud motors are powered by hydraulic energy from the drilling mud. High-pressure mud is pumped down the drill string and through the motor, causing internal components to move and generate rotation.
In simple terms: Mud motors are like underground drills powered by mud, helping us steer and dig tunnels for pipes and cables without digging up the whole surface.
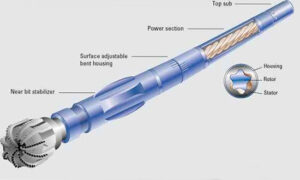
2. Structure (结构 – Simplified):
While mud motors have complex internal workings, here’s a simplified view of their main parts:
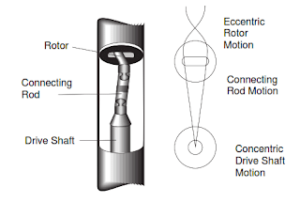
Stator and Rotor (定子和转子): These are the heart of the motor. The stator is a stationary part with a special internal shape. The rotor is inside the stator and is free to rotate. Mud flowing through the stator and rotor creates pressure differences that make the rotor spin. Think of it a bit like a water turbine.
Bearing Assembly (轴承组件): Bearings are crucial for supporting the rotating parts (like the rotor and drive shaft) and allowing them to spin smoothly and reliably under load. These bearings need to withstand high pressure, abrasive mud, and heavy loads.
Drive Shaft (传动轴): This shaft connects to the rotor and transmits the rotational power from the motor to the drill bit.
Housing (外壳): A strong outer casing protects the internal parts of the motor from the harsh underground environment and drilling mud. Sometimes the housing is slightly bent in steerable motors.
Mud Inlet and Nozzle (泥浆入口和喷嘴): This is where the high-pressure drilling mud enters the motor. Nozzles control the mud flow and pressure inside the motor.
Think of it like this: Mud pushes the rotor inside, making it spin, and that spin drives the drill bit to cut through the ground.
Mud Motor Operation User Guide
1. Back reaming with motor is prohibited. Slurry is recommended as drilling fluid.
After completing each steering (or pilot drilling) section, be sure to remove the mud motor before proceeding with pullback operations. Pulling back with the motor attached can cause stress concentration, leading to motor fracture or damage.
The drilling fluid of choice is mud. Select a mud pump with a corresponding displacement and model to drive it (see attached diagram 2.). Insufficient pump discharge flow can cause the motor to fail to start, or for the motor to lock up during drilling, resulting in no penetration (advance). Unstable pump discharge flow can cause the motor to operate intermittently, starting and stopping.
Another possible reason for poor mud pump discharge is partial blockage by large, hard rock particles forming within the drill pipe and motor, or between the probe housing and the drill pipe. This intermittent blockage causes the mud to flow intermittently, leading to unstable rotation speed. In such cases, it is best to disassemble and inspect the motor, drill pipe, and probe housing, and to clear any internal debris until the mud flows smoothly.
2. Flow rate of pump should not be lower than 600L/M, or the motor cannot be driven, or be locked in drilling process.
| Mud Motor
(mm) |
95 | 120 | 165 | 172 |
| Flow rate of Mud pump
(L/M) |
≥600 | ≥800 | ≥1300 | ≥1300 |
Diagram 4. selection of mud pump for mud motor
3. A new or idle motor should be rotated clockwise at least 2 rounds with a tong before working with a pump.
In on-site operations, first use a pipe wrench(or a hydraulic tong) to rotate the spindle head clockwise for more than 2 turns before starting pump circulation.
4. After use, user shall clean it internally. Rotate the drive axle to remove the residual fluid.
After using the motor, be sure to clean out internal debris with clean water. After detaching the motor, use a pipe wrench to rotate the drive shaft clockwise to purge any residual fluid from inside the motor. Otherwise, the motor may fail to start when used again.
5. Drive axle of this motor is open for lubrication, hence fluid leak is normal.
Due to the open structure of the mud motor’s drive shaft section, the design allows for mud to leak from the gap between the drive shaft and the bearing housing. This leaked mud serves to lubricate and cool the TC bearings in the drive shaft area, preventing bearing seizure caused by excessive friction heat. Generally, this mud leakage is a normal phenomenon (leakage should not exceed 6% of the mud motor’s normal operating flow rate).






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.